
As the molecular interactions decrease with decreasing concentrations, viscosity measurements are carried out with very dilute solutions. The flow behavior of the polymer solution is highly dependent on the molecular structure of the polymer as well as on interactions of the molecules with each other in solution. One of those is “dilute solution viscometry,” which can determine parameters such as intrinsic viscosity. įor the characterization of synthetic polymers as well as biopolymers, many different techniques are available. In addition, they are used as industrial plastics, clothing fabrics, absorbents, water treatment chemicals, or biosensors in other applications. More specifically, biocompatible and biodegradable biopolymers are suitable for applications such as edible films, emulsions, or packaging materials in the food industry as well as wound dressing materials, medical implants, sutures, or drug transport materials in the pharmaceutical and medical industries. Due to these beneficial properties, biopolymers can be used in different application areas, such as the food, medical, and pharmaceutical industries. In comparison to synthetic polymers, biopolymers offer advantages like well-defined and more-complex structures, (bio)degradability, non-toxicity, and renewability. This definition includes proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides. e., macromolecules that are formed by living organisms). Īccording to IUPAC, biopolymers are substances that are composed of one type of biomacromolecules (i.

To meet this demand for alternative materials for specific applications, many different biopolymers and renewable resource-based biopolymers have been studied and developed.
For such materials, these should not only be biodegradable but also be derived from natural resources. Since they are typically derived from fossil raw materials, however, synthetic polymers are increasingly being replaced by biodegradable materials because of environmental concerns. When it comes to applications like food packaging, synthetic polymers are mostly used for them because of certain benefits these polymers offer, including versatility, functionality, affordability, and flexibility. Depending on the type of monomer as well as the size and molecular structure of the polymer molecule, polymers show unique properties. Polymers are macromolecules that are composed of small repeating units called “monomers” (Figure 1). Intrinsic viscosity is used to classify polymers and helps to identify the applications that specific polymers can be used for. In the kinematic measuring method, gravity is the only force that acts on the sample.Intrinsic viscosity determination is used in the field of polymer chemistry, which is a chemistry subdiscipline that deals with the synthesis of polymers as well as the analysis of a polymer’s structure and properties. The mass (or weight) of a fluid is determined by gravity. Therefore, we say that steel has a greater density than ice cube. They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube. Think about an ice cube and a cube of steel.
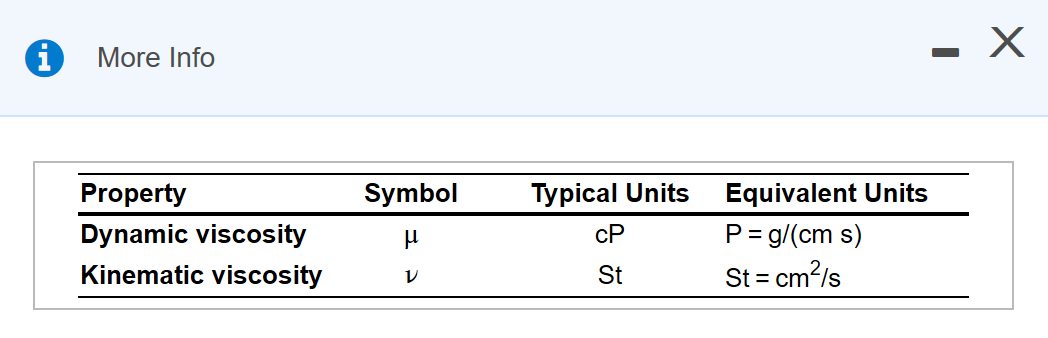
The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. One way is to measure a fluid’s resistance to flow when an external force is applied. Water at 20 ☌ has a kinematic viscosity of about 1 cSt. Other units are: 1 St ( Stoke) = 1 cm 2/s = 10 −4 m 2/s. The SI unit of the kinematic viscosity is m 2/s. The kinematic viscosity is the ratio between the dynamic viscosity and the density of a fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
